Introduction
Understanding the differences held between viruses and malware has not been of particular nor pressing concern for the average global citizen up until perhaps a few years ago.
However, with the rapid surge in digital and cyber threats becoming rampantly abundant, millions of computer users across the globe began self-educating themselves on the intricacies of at-home cybersecurity to protect their finances, personal information, and much more.
In today’s modern times, keeping abreast of the distinctions between the various concepts in cybersecurity are of paramount importance.
Due to the ever-evolving cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated and harder to fight, the heightened risk to the data we hold dear in our lives can become compromised without the proper knowledge and management involved with protecting yourself in today’s cyber world.
What is Malware?
Malware is a condensed version of the term malicious software and is an umbrella term referring to several different classes of dangerous cyber threats, including, but not limited to, Trojans, viruses, worms, and bots, as well as adware and spyware
A slightly more advanced form of malware, ransomware, is purposed by hackers to commit fraud, extortion, and theft from computer users.
Not only are there a multitude of malware in existence but many of them have sophisticated ways of propagating themselves.
According to Cisco.com, malware is “specifically designed to damage, disrupt, steal, or in general inflict some other “bad” or illegitimate action on data, hosts, or networks.”

Types of Malware
As mentioned above, there are several classes of malware. Each class of malware has a distinct method it employs to try to gain entry into your system or network. The types of malware most prevalent in 2018 are the following:
- Viruses
- Worms
- Bots
- Ransomware
- Backdoors
- Spyware
- Adware
Malware has the potential to infect a system through the following:
- Malware can breach systems by being bundled and “enshrouded” with a host of other legitimate programs attached as files or macros
- Malware can be installed inadvertently by a user visiting a website designed for the sole intent of infecting it’ visitors with malware
- Malware can be found on computers by other inadvertent actions y users, such as the clicking of a malicious email link, attachment, picture, or via download
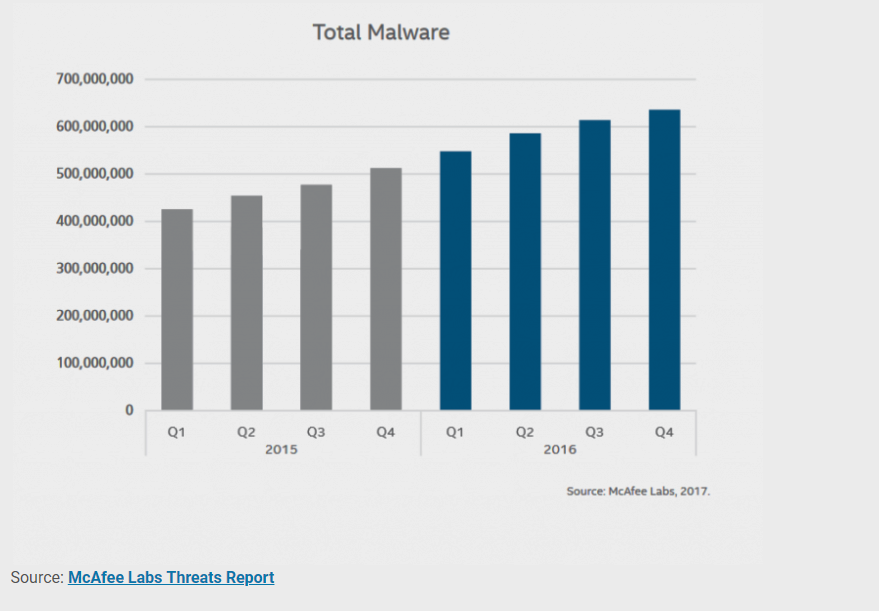
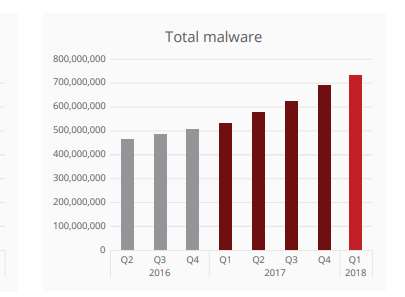
The chart shown above from McAfee Labs is their annual “Threats Report” compilation, totaling the number of major cybersecurity threat occurrences each year across the globe
In the span of a year, global malware threats shot up by over an astounding two hundred million cases. The Threat Report for 2018 is truly eye-opening, however, as it shows an increase of over well over one hundred million major malware threat attempts.
However, the importance of this graph is clear: malware isn’t going anywhere. In fact, it has been climbing by a rate of over one hundred million cases per year and is anticipated by industry analysts to grow to near insurmountable levels in the 2020s
Much more than just a trend, malware is a force of terrorism, putting digital users of all ages, backgrounds, and cultures at risk every moment of every day.
To put the matter into perspective even further, consider Accenture’s recent statement that malware attacks are among the most costly cyber attacks in existence today, with companies spending upwards of 2.4 million dollars in protective measures.
What’s Going on With Malware Today?
- According to Symantec, “Variants of mobile malware increased by 54 percent in 2017-2018
- 2017 reflected a whopping 80% increase in malware instances found o Mac computers
- Today in 2018, one in every thirteen web requests ultimately lead to malware, which is an increase of three percent from 2016
Additional Important Information About Malware
Computer users that aren’t well seasoned in the cyber security sphere and its associated lexicon often confuse malware as a form of defective software containing errors.
Holding this oversimplified view is immensely detrimental, as unknowing users can become the recipients of successful malware attacks that have now evolved to the extent that they can damage the software, data, and even the physical hardware components of a user’s system.
Successful malware attacks made on businesses pose a much greater spectrum of consequences, including, but not limited to, substantial losses in data, an array of financially-related issues, an operation that has been thoroughly disrupted, and worst of all, the potential for a company’s site to go into “downtime” mode and become aired by major news networks.
Malware attacks may number into the hundreds of millions, but instances of actual breaching are far fewer. According to Varonis.com, between January 1, 2005, and April 18, 2018, there have been 8,854 recorded breaches.

Computer virus protection concept. Alert of hacker attacks on the laptop screen
Some of the most famed instances of successful malware attacks in recent times include the following:
- Yahoo – 2016: In what’s been referred to as one of the biggest security breaches of all time, Yahoo was successfully hacked into and resulted in the compromising of over three billion user accounts and their associated details
- Uber – 2016: Uber lost much of its good standing when hackers successfully accessed the personal information and details of fifty-seven million drivers and users
- FriendFinder – 2017: This popular networking site was hacked into, ultimately exposing the account and personal details of well over four hundred million users
- Equifax- 2017: Equifax headquarters were breached in late 2017, ultimately negatively impacting nearly one hundred and fifty million consumers of the service
- My Fitness Pal – 2018: Owned by Under Armor and home to an enormous subscriber base, this popular app was hacked, immediately putting one hundred at fifty people at risk
Quick Review and Lesson
Prior to delving into the subject of viruses, their distinctions, and their relationship to malware, we’d like you to engage in a quick review lesson that will help your better incorporate and digest the next part of this article, while making your own comparisons and contrasts in your mind as you read on to the end conclusion of the article.
Lesson #1: MALWARE is an umbrella term for software designed for malicious intent, including things like VIRUSES, worms, bots, ransomware, backdoors, spyware, adware and more
- Note: Think of Malware as a bucket filled with various infectious bugs, including viruses.
Lesson #2: VIRUSES are a type of MALWARE, just like ransomware and worms are types of malware.
- Note: A virus is a piece of harmful software that is often capable of self-replicating and can spread through computers, networks, and the internet through virus-infected downloads, attachments, files, and documents
Lesson #3: Always remember the following: VIRUSES are a type of MALWARE

Viruses as demonstrated above in the review lesson, are a type of malware. It has an infectious component to it and spreads easily from system to system at lightning speed under the right conditions.
In particular, when virus-infected software is widely shared with others, albeit unintentionally, viruses can begin spanning entire nations or even the globe.
Often compared to a parasite, viruses join other “gnarly insects” in the Malware class, right alongside Trojan Horses, spyware, adware, and worms – all employing differential tactics to gain entry into computer users systems, create harm, and steal information.
Viruses
What are viruses exactly? Viruses can wreak havoc and destruction on computers, a range of digital devices, and even an entire network.
A virus that has successfully infected its target can potentially result in the loss of data, a reduction in computer and business performance, and the compromising of sensitive data pertaining to the company and its clients.
From there, a virus can propagate itself, moving from victim to victim via email attachments, files, documents, and downloads; traveling through the internet and the world at large.
More specifically defined, a computer virus is a form of malicious software that is designed and executed by hackers at “opportune” times (timing can be based on gaining the most resources and data or perhaps even the most international visibility).
Upon execution, a computer virus begins to self-replicate while also modifying computer or device programming and re-inserting with its own malicious, self-serving code.
The point at which replication succeeds is considered to be a success, with the targeted areas of a system satisfactory infected, and thus leading to the official diagnosis of the computer as “infected.”
What can viruses result in: Computer viruses that occur in today’s times can cost billions of dollars in damages for businesses, due in large part to the large assortment of costs involved, which can include the following:
- System damage or failure
- Network damage
- The exorbitant costs of attempting to recover data
- The costly waste of computer resources
- Maintenance costs
- Repair costs
- Replacement costs
- Consultancy costs
- Corrupted or lost data
- Lost customers
- Reduced financial bottom line from lack of trustworthiness by consumers
- Building a resilience plan for the future to prevent similar future circumstances
How many viruses out there? In the year 2000, there were a spectacular 40,000 computer viruses in existence. In 2003, that number jumped to just over 103,000.
In 2008, Symantec reported that the number of viruses in existence today exceeds well over a million. Important to note, however, is that only a very small percentage of those viruses are still in circulation and are worth reading up on.

What kinds of viruses are there, and which viruses should I know about? You should be aware of some of the more common viruses in existence right now (listed right below) in addition to the infamous viruses that caused great financial harm to countless people around the world. These viruses are listed in the next section’s chart.
Common Viruses You Should Know About Today
| Virus Name | Key Points |
| MDMA | Transferred via MS Word file to another MS File only if both files are stored in memory |
| Melisa | Distributed as an email attachment; takes on different functions with the presence of MS Outlook, disables safeguards |
| Ripper | Shreds and corrupts data from the hard disk, rendering it irretrievable |
| SirCam | Is sent via email attachment; capable of deleting files at will, destroying performance levels, and sending files on its own |
| Concept | Transferred via email attachment; saves files in a template directory as opposed to its original, intended location |
| Nimba | Multifaceted virus that damages computers substantially, as well as altering many of its settings |
| One_Half | Encryption-capable renders data readable only by the virus hard disk so only the virus may read the data. |
| CodeRed | Impacts Microsoft II servers; enables remote access after hacking; was used on an attack on the White House |
Most Infamous Viruses of All Time
| Virus name | Interesting facts | Related figures |
| I Love You | Guinness World Record’s entry as the most ‘virulent’ virus of all time | $15 billion in damages |
| MyDoom | Regarded as the most damaging virus ever released | $38 billion in damages |
| Wannacry | Impacted 100,000 groups in 150 countries and over 400 million devices | $4 billion in damages |
| Slammer | Crashed the internet for 15 min, brought down Bank of America’s ATM services, disrupted 911 emergency services, and even caused lights to go out in several cities | 1 billion in damages |
Types of Viruses You Don’t Need To Worry About As a Novice or At-Home User
| Name | Name |
| Multipartite Virus | File Infector Virus |
| Resident Virus | Direct Action Virus |
| Boot Sector Virus | Polymorphic Virus |

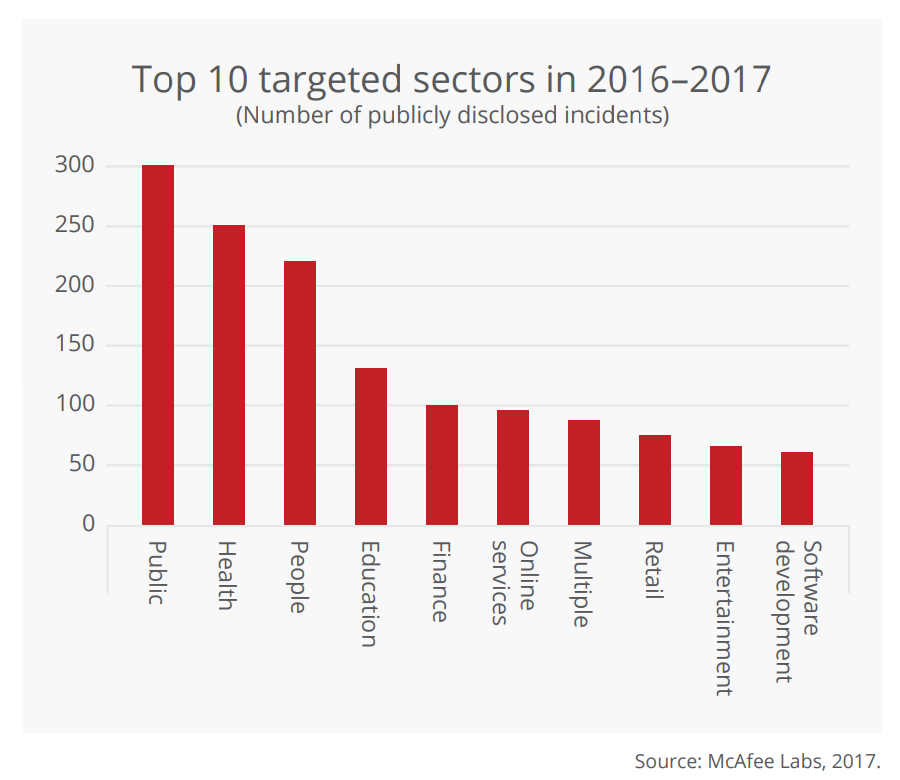
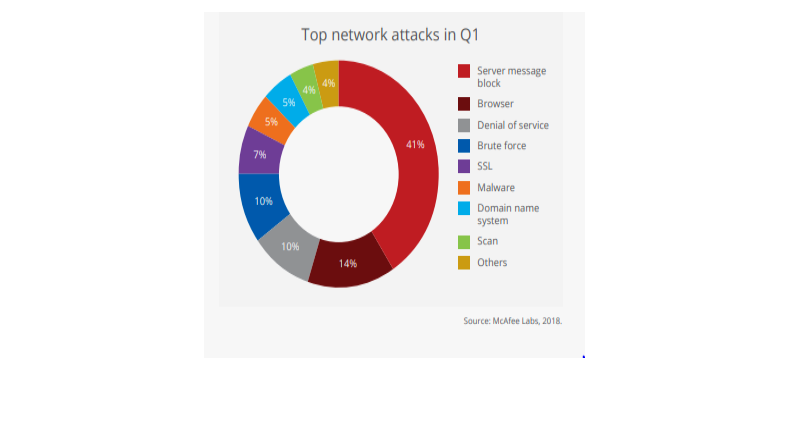
What’s going with viruses today? Quite a bit. As the infographics below show, viruses have been going after many sectors, including the banking arena, and hackers are using a variety of attacks to gain entry into sites.
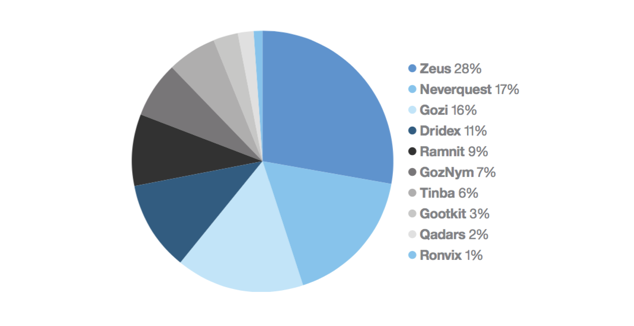
Top Ten Viruses Impacting Banking Institutions for 2017-2018
Top Ten Targeted Sectors in 2017-2018
Top Types of Network Attacks in 2018 Q1
The Bottom Line
Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly skilled at their trade, using tactics that display astounding levels of sophistication and complexity.
As a result, it has never been more abundantly clear that we need to protect ourselves in every possible from the looming threats of numerous and varying cyber dangers.
Protecting our computers, devices, and networks have now become of paramount importance in these technological times for all the types of people, from businesses, government agencies, and perhaps most importantly, at-home users who have the most to lose, as well as the most incentive to learn the very best protection measures readily available today.

